Product Description
Steering Shaft Universal Joints Coupling Pin for Gimbal Cardan Drive Shaft
| Product: | Universal Coupling |
| Model: | HZLSJU002 |
| Size: | 3/4-36 Spline X 3/4″ DD |
| Delivery Date: | 30 Days |
| MOQ: | 30 sets or according to stocks without minimum Qty. |
| Sample: | Acceptable |
| We could produce all kinds of universal coupling according to customers’ requirement. | |
About us
We have more than 17 years experience of Spare parts, especially on Drive Line Parts.
We deeply participant in the Auto Spare parts business in HangZhou city which is the most import spare parts production area in China.
We are supply products with good cost performance for different customers of all over the world.
We keep very good relationship with local produces with the WIN-WIN-WIN policy.
Factory supply good and fast products;
We supply good and fast service;
And Customers gain the good products and good service for their customers.
This is a healthy and strong equilateral triangle keep HangZhou Speedway going forward until now.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Standard Or Nonstandard: | Nonstandard |
|---|---|
| Shaft Hole: | 30mm |
| Torque: | 10-30N.M |
| Bore Diameter: | 30mm |
| Speed: | 3000 |
| Structure: | Flexible |
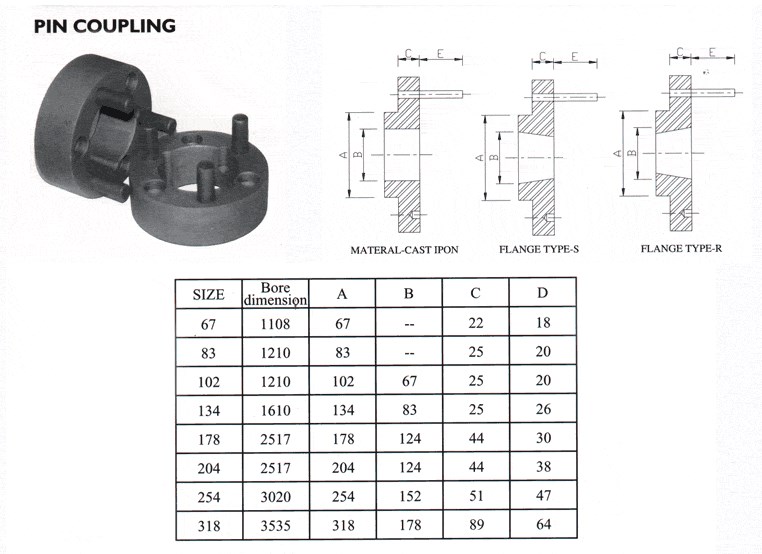

What Are the Maintenance Requirements for Pin Couplings?
Pin couplings are known for their simplicity and ease of maintenance. Regular maintenance helps ensure the longevity and optimal performance of pin couplings in various mechanical systems. Here are the key maintenance requirements for pin couplings:
- Lubrication: Most pin couplings require periodic lubrication to reduce friction between the pins and the coupling hubs. Lubrication helps prevent wear and corrosion, ensuring smooth operation.
- Inspection: Regular visual inspections are essential to identify any signs of wear, misalignment, or damage. Inspecting the pins, coupling hubs, and surrounding components can help detect potential issues early on.
- Torque Check: It is crucial to periodically check and retighten the bolts or screws that secure the coupling to the shafts. Loose fasteners can lead to misalignment and coupling failure.
- Alignment: Proper shaft alignment is critical for the effective functioning of pin couplings. Regularly check and adjust the alignment if necessary to minimize wear and vibrations.
- Environmental Protection: In harsh environments or corrosive conditions, take measures to protect the pin coupling from contaminants or chemicals that could cause damage.
- Replacement of Worn Components: When any of the coupling components, such as pins or hubs, show signs of significant wear, they should be replaced promptly to prevent further damage.
It is important to follow the manufacturer’s maintenance guidelines and recommendations for the specific type of pin coupling used in the application. Regular maintenance not only ensures the smooth operation of the coupling but also helps prevent unexpected breakdowns and reduces the risk of costly downtime. Proper maintenance can extend the service life of pin couplings and contribute to the overall reliability of the connected equipment.

How Does a Pin Coupling Handle Angular, Parallel, and Axial Misalignment?
A pin coupling is designed to handle different types of misalignment, including angular, parallel, and axial misalignment. The unique construction of pin couplings allows them to accommodate these misalignments without compromising the efficiency and performance of the connected equipment.
1. Angular Misalignment: Angular misalignment occurs when the axes of the driving and driven shafts are not parallel but intersect at an angle. Pin couplings can tolerate angular misalignment because of their flexible and floating pin design. The two coupling halves are connected by a series of pins, which can pivot and move within the pin holes. This flexibility allows the coupling to bend slightly, adjusting to the angle of misalignment between the shafts.
2. Parallel Misalignment: Parallel misalignment happens when the axes of the driving and driven shafts are parallel, but they are laterally displaced from each other. Pin couplings can handle parallel misalignment to some extent due to the floating nature of the pins. The pins can move laterally within the pin holes, allowing the coupling to adapt to the offset between the shafts.
3. Axial Misalignment: Axial misalignment occurs when there is a linear displacement along the axis of one shaft concerning the other. While pin couplings primarily focus on handling angular and parallel misalignment, they may offer limited axial misalignment capabilities. The floating pins provide a small degree of axial movement, but excessive axial misalignment is best avoided to prevent additional stresses on the coupling.
It is important to note that while pin couplings can accommodate some degree of misalignment, excessive misalignment should be avoided to prevent premature wear and potential failure of the coupling and connected equipment. Regular inspection and maintenance can help identify and address any misalignment issues, ensuring the optimal performance and longevity of the pin coupling in power transmission applications.
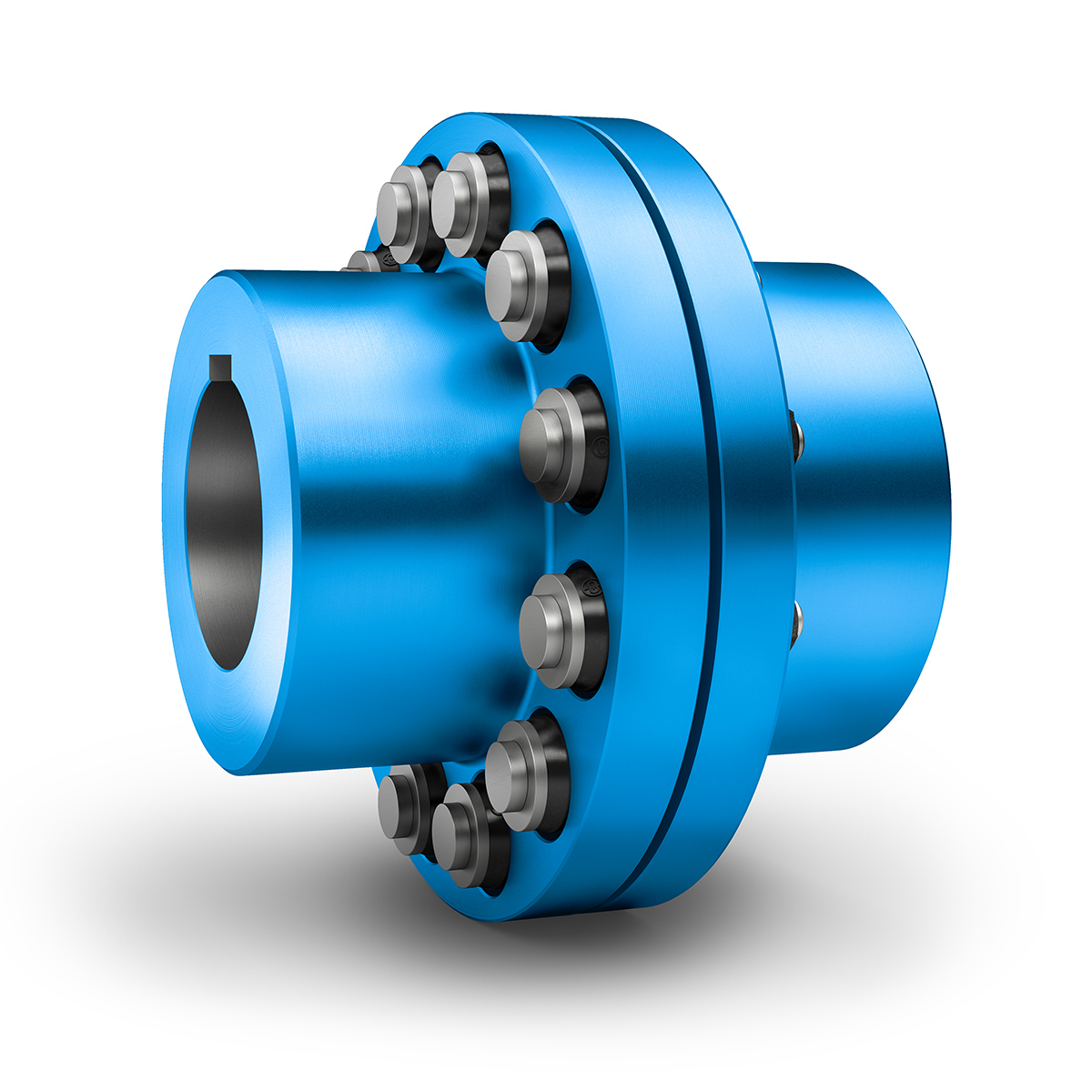
Selecting the Appropriate Pin Coupling for a Specific Application
Choosing the right pin coupling for a specific application involves considering several factors to ensure optimal performance, reliability, and safety. Here are the key steps to select the appropriate pin coupling:
- 1. Determine the Application Requirements: Understand the specific requirements of the application, including torque and speed specifications, shaft sizes, and misalignment tolerances. Consider the operating conditions, such as temperature, humidity, and exposure to corrosive substances.
- 2. Calculate Torque and Power: Calculate the torque and power requirements of the application to determine the appropriate pin coupling’s torque capacity. Make sure to consider both steady-state and peak torque loads.
- 3. Consider Misalignment Tolerance: Evaluate the degree of misalignment expected in the system. Different pin coupling designs offer varying levels of misalignment tolerance. Choose a coupling that can accommodate the expected misalignment without compromising performance.
- 4. Select the Pin Coupling Type: Based on the application requirements, choose the appropriate pin coupling type – single pin, double pin, triangular pin, splined pin, or taper pin coupling. Each type offers different torque capacities and misalignment capabilities.
- 5. Check Material and Construction: Consider the materials used in the pin coupling’s construction. Common materials include steel, stainless steel, and alloy materials. The material should be suitable for the application’s environmental conditions and corrosion resistance.
- 6. Verify Safety Features: Ensure the selected pin coupling has safety features, such as a fail-safe mechanism to protect equipment from overload or shock loads. Safety is crucial to prevent damage to machinery and ensure operator protection.
- 7. Consult with Manufacturers or Engineers: If unsure about the best pin coupling for the application, consult with coupling manufacturers or mechanical engineers. They can provide valuable insights and recommendations based on their expertise.
By following these steps, you can select the appropriate pin coupling that matches the specific needs of the application, providing reliable and efficient power transmission while minimizing the risk of downtime and equipment failure.


editor by CX 2024-04-08